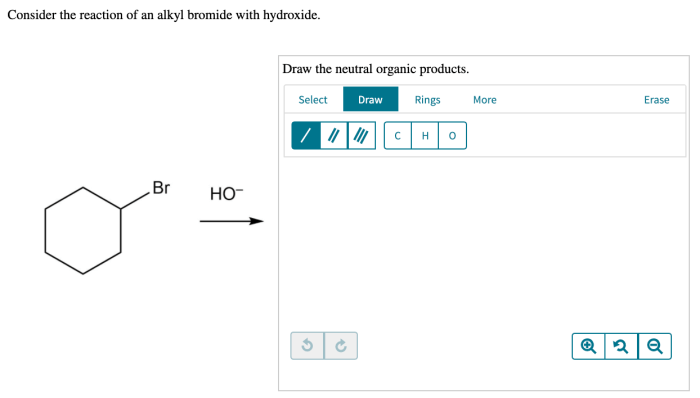
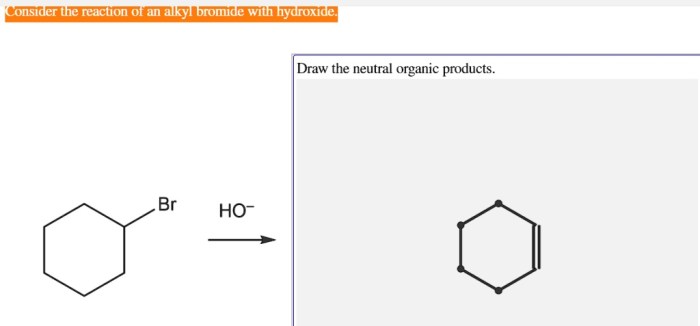
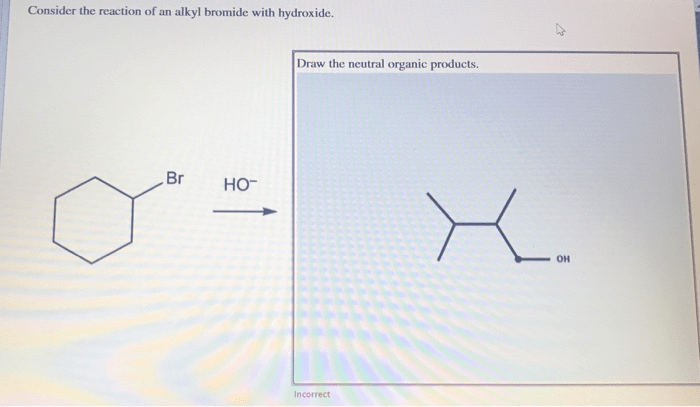
Consider the reaction of an alkyl bromide with hydroxide. – Consider the reaction of an alkyl bromide with hydroxide, a fundamental concept in organic chemistry. This reaction, characterized by its nucleophilic substitution mechanism, plays a pivotal role in various chemical transformations. Delving into the intricacies of this reaction, we will explore the properties of the reactants, elucidate the reaction mechanism, and discuss the factors influencing its outcome.
Alkyl bromides, bearing a halogen atom bonded to an alkyl group, exhibit varying reactivity based on the alkyl group’s size and substitution pattern. Hydroxide, on the other hand, is a strong base commonly encountered in aqueous solutions. Understanding the properties of these reactants is crucial for comprehending their behavior in this reaction.
Alkyl Bromide
Alkyl bromides are organic compounds that contain a bromine atom bonded to a carbon atom in an alkyl group. They are typically colorless liquids or solids with a pungent odor. Alkyl bromides are widely used in organic synthesis as alkylating agents.
The general structure of an alkyl bromide is R-Br, where R is an alkyl group. Alkyl groups can be primary (1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°). The reactivity of alkyl bromides decreases as the number of alkyl groups attached to the carbon atom bearing the bromine atom increases.
Some common examples of alkyl bromides include:
- Methyl bromide (CH 3Br)
- Ethyl bromide (CH 3CH 2Br)
- Isopropyl bromide ((CH 3) 2CHBr)
- tert-Butyl bromide ((CH 3) 3CBr)
Hydroxide
Hydroxide is a negatively charged ion with the formula OH –. It is the conjugate base of water and is formed when water undergoes ionization. Hydroxide ions are highly reactive and can react with a variety of compounds.
Hydroxide ions are found in many natural and industrial processes. They are essential for the functioning of many biological systems and are used in a variety of industrial applications, such as the production of paper, textiles, and soap.
Hydroxide ions are highly reactive and can react with a variety of compounds. They can react with acids to form salts and water, with metals to form metal hydroxides, and with organic compounds to form a variety of products.
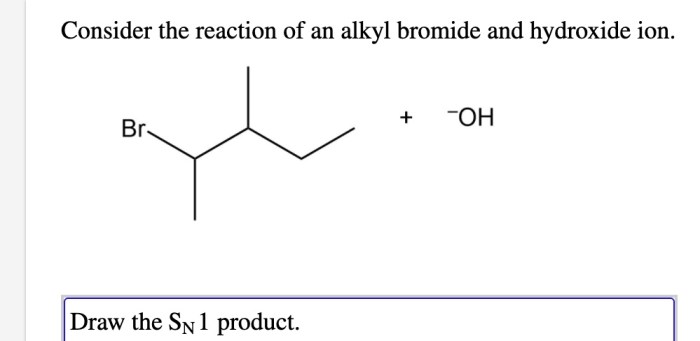
Reaction of Alkyl Bromide with Hydroxide: Consider The Reaction Of An Alkyl Bromide With Hydroxide.
The reaction of an alkyl bromide with hydroxide is a nucleophilic substitution reaction. In this reaction, the hydroxide ion attacks the carbon atom bearing the bromine atom, displacing the bromine atom and forming an alcohol.
The mechanism of the reaction is as follows:
- The hydroxide ion attacks the carbon atom bearing the bromine atom, forming a tetrahedral intermediate.
- The bromine atom is displaced from the tetrahedral intermediate, forming an alcohol and a bromide ion.
The reaction of an alkyl bromide with hydroxide is a versatile reaction that can be used to synthesize a variety of alcohols. The reaction is typically carried out in a polar aprotic solvent, such as dimethylformamide (DMF) or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
Some examples of the reaction of an alkyl bromide with hydroxide include:
- Methyl bromide + hydroxide → methanol + bromide ion
- Ethyl bromide + hydroxide → ethanol + bromide ion
- Isopropyl bromide + hydroxide → isopropanol + bromide ion
- tert-Butyl bromide + hydroxide → tert-butanol + bromide ion
Factors Affecting the Reaction
The rate of the reaction between an alkyl bromide and hydroxide is affected by a number of factors, including:
- Temperature:The rate of the reaction increases with increasing temperature.
- Solvent:The rate of the reaction is faster in polar aprotic solvents, such as DMF or DMSO, than in protic solvents, such as water or methanol.
- Concentration:The rate of the reaction increases with increasing concentration of the alkyl bromide and hydroxide ion.
These factors can be used to control the rate of the reaction and to optimize the yield of the desired product.
Applications of the Reaction
The reaction of an alkyl bromide with hydroxide is a versatile reaction that has a wide range of applications in organic synthesis. The reaction is used to synthesize a variety of alcohols, which are important intermediates in the synthesis of many other organic compounds.
Some of the applications of the reaction include:
- Synthesis of alcohols:The reaction of an alkyl bromide with hydroxide is the most common method for the synthesis of alcohols.
- Alkylation of other compounds:The reaction of an alkyl bromide with hydroxide can be used to alkylate other compounds, such as amines and thiols.
- Polymerization:The reaction of an alkyl bromide with hydroxide can be used to polymerize alkenes and alkynes.
FAQ Insights
What is the general mechanism of the reaction between an alkyl bromide and hydroxide?
The reaction proceeds via a nucleophilic substitution mechanism, where the hydroxide ion attacks the electrophilic carbon of the alkyl bromide, leading to the formation of an alcohol and bromide ion.
How does the structure of the alkyl bromide affect the reaction rate?
Primary alkyl bromides react faster than secondary alkyl bromides, which in turn react faster than tertiary alkyl bromides. This is due to the increasing steric hindrance around the electrophilic carbon as the alkyl group becomes more substituted.
What are some applications of the reaction between an alkyl bromide and hydroxide?
This reaction is widely used in organic synthesis for the preparation of alcohols, ethers, and other organic compounds. It also finds applications in the production of pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and polymers.